Climate Change Knowledge.org
FEED BACKS
science




Climate feedback
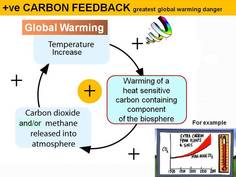
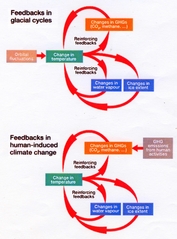
An interaction mechanism between processes in the climate system is called a climate feedback, when the result of an initial process triggers changes in a second process that in turn influences the initial one. A positive feedback intensifies the original process, and a negative feedback reduces it. IPCC
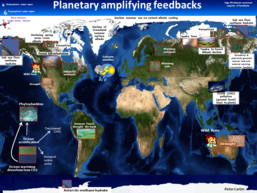
Global climate change science is all about feed-backs. In fact the large temperature swings fronm ice ages into warm periods like now is the result of +ve feed-backs- loss of ice sheet albedo cooling, increase methane and increase CO2. from planetary feedback sources (bottom of page)..
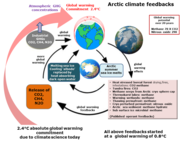
Climate change impacts is all about the many large positive amplifying feed-backs. The largest feed-backs are not accounted for in climate change assessments of the projected global temperature increases.
A positive (bad) amplifying happens when global warming causes an increase in the degree of warming (or acceleration of the rate of warming).
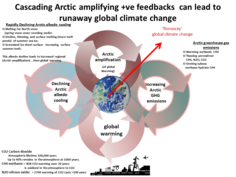
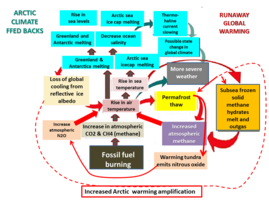
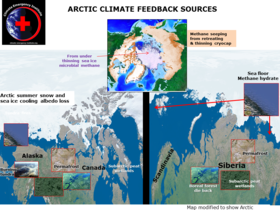
It is the multiple large +ve Arctic feed-backs that could cause abrupt warming and so called runaway climate change which would total planetary catastrophe for most life.
An interaction mechanism between processes in the climate system is called a climate feedback, when the result of an initial process triggers changes in a second process that in turn influences the initial one. A positive feedback intensifies the original process, and a negative feedback reduces it. IPCC
Global climate change science is all about feed-backs. In fact the large temperature swings fronm ice ages into warm periods like now is the result of +ve feed-backs- loss of ice sheet albedo cooling, increase methane and increase CO2. from planetary feedback sources (bottom of page)..
Climate change impacts is all about the many large positive amplifying feed-backs. The largest feed-backs are not accounted for in climate change assessments of the projected global temperature increases.
A positive (bad) amplifying happens when global warming causes an increase in the degree of warming (or acceleration of the rate of warming).
It is the multiple large +ve Arctic feed-backs that could cause abrupt warming and so called runaway climate change which would total planetary catastrophe for most life.
The first +ve feedback is from water vapour which is a greenhouse gas.
The warmed atmosphere can hold more water vapor which increases the warming from the addition of a greenhouse gas alone.
The water vapor increase about doubles the greenhouse gas warming.
The warmed atmosphere can hold more water vapor which increases the warming from the addition of a greenhouse gas alone.
The water vapor increase about doubles the greenhouse gas warming.
The largest +ve feed backs are Arctic (see below).
+ve feed backs (amplify warming)
water vapor
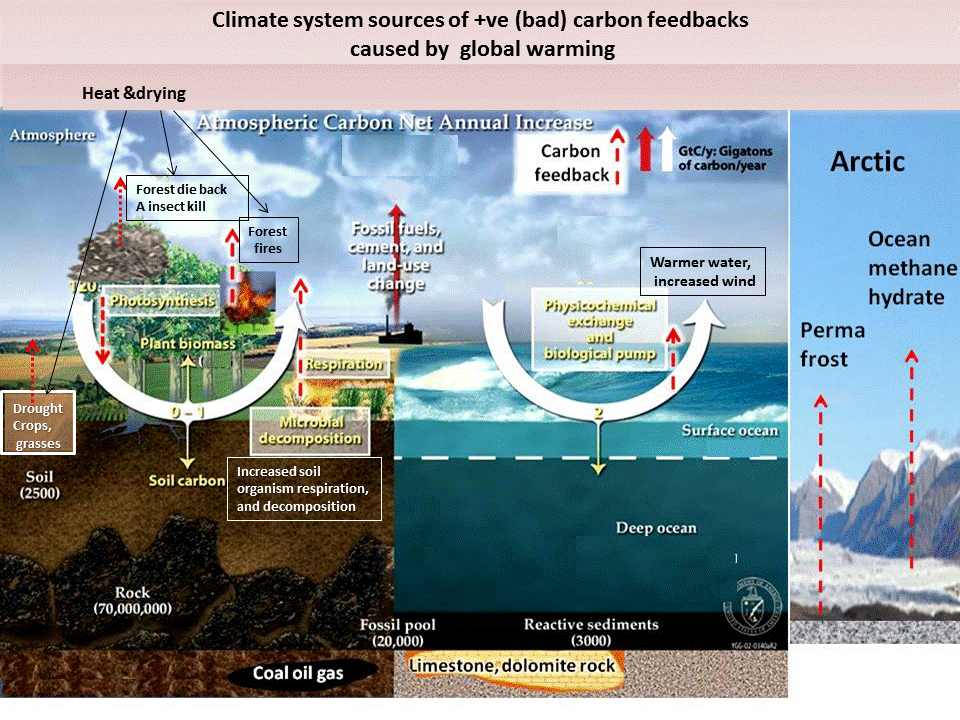
terrestrial carbon (soil, vegetation excluding peat lands and Arctic
forest fires
doughts (less CO2 uptake)
ground level ozone (toxic to green plants
reducing CO2 uptake)
warming peat lands (methane)
warming global wetlands (excl peat land
methane)
Thawing permafrost
Sea floor methane hydratre
Snow melting (albedo loss)
Ice melting (esp Arctic summer sea ice)
+ve feed backs (amplify warming)
water vapor
terrestrial carbon (soil, vegetation excluding peat lands and Arctic
forest fires
doughts (less CO2 uptake)
ground level ozone (toxic to green plants
reducing CO2 uptake)
warming peat lands (methane)
warming global wetlands (excl peat land
methane)
Thawing permafrost
Sea floor methane hydratre
Snow melting (albedo loss)
Ice melting (esp Arctic summer sea ice)
Arctic +ve feedbacks
Runaway
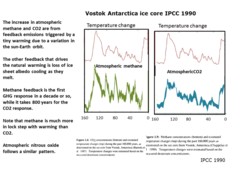
The large temperature swings from ice ages into warm periods like now is the result of +ve feed-backs.
These are loss of ice sheet albedo cooling, increase methane and increase CO2. from planetary feedback sources
These are loss of ice sheet albedo cooling, increase methane and increase CO2. from planetary feedback sources